Introduction:
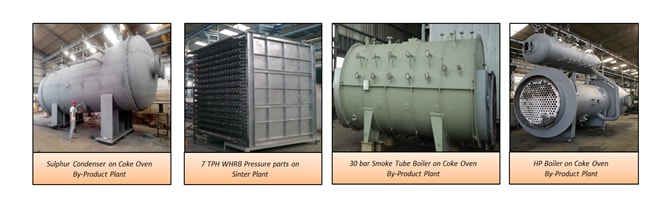
Modern steel plants generate huge profits from energy savings and sale of by-products or rather, the profitability of steel plants hinges upon energy recovery and sale of by-products today. Huge opportunities exist in recovering waste heat from almost all processes in an integrated steel mill – Coke Oven, Blast Furnace, Electric Arc Furnace, Basic Oxygen Furnace and of course, the Sinter Plant.
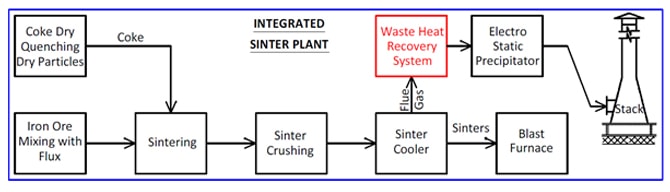
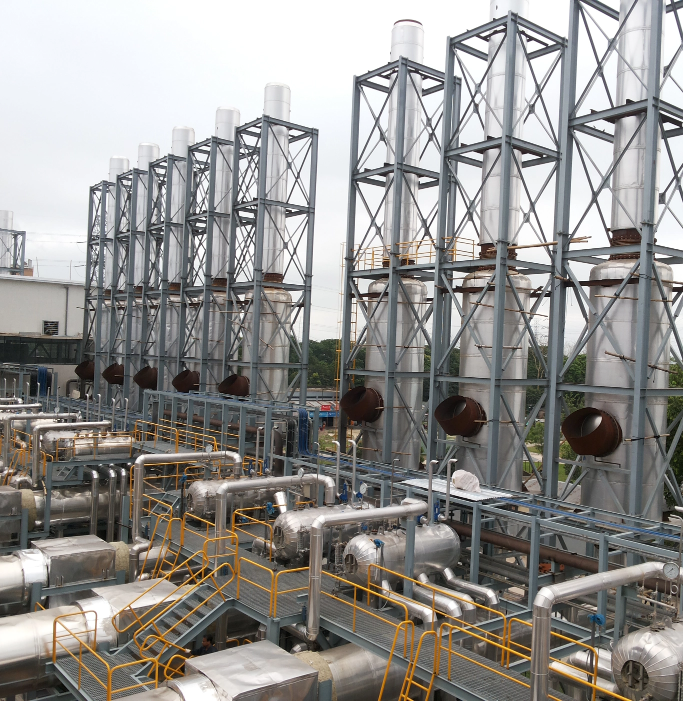
Sinter Plant Waste Heat Recovery System:
Iron ore fines along with flux and coke fines or coal are heated to produce a semi-molten mass that solidifies into porous pieces of sinter with the size and strength characteristics necessary for feeding into the blast furnace. The sinter so produced is crushed and discharged into a sinter cooler, where it is cooled by using a forced draught fan. The ambient air gets heated up to approximately 400°C in this process. The mass flow rate of this cooling air being extremely large, the amount of heat energy that can be recovered and reutilized is enormous! The hot air emerging out from the cooler has very high dust concentration, up to 4,000 mg/Nm3, and the WHRB is well designed to take care of the fouling and environmental concerns.
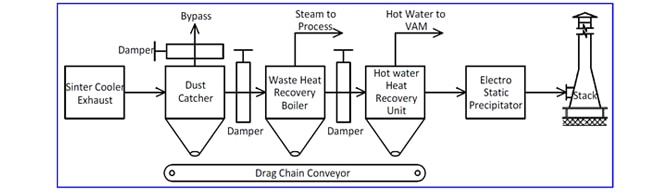
Two Stage Heat Recovery System:
The Hot exhaust gases from the Sinter Cooler first enter a mechanical dust collection device and then a well-designed WHRB to generate Superheated or Saturated steam, as per the plant requirement. Even after the WHRB recovering maximum heat feasible technically, the existing gases have large amount of low grade heat. This heat is recovered by a Hot Water Heat Recovery Unit (HW HRU) downstream the WHRB, as hot water circulating in a closed loop system. The steam thus generated could be put to use in the plant and the Hot water is used as energy source for Vapour Absorption Chiller. The system is well-equipped with necessary instrumentation and a PLC based system for safety & controls, monitoring and diagnostics. Downstream of these systems, an Electro Static Precipitator is provided prior to gases exiting through Chimney.
Typical System Parameters of a WHR System:
The Hot exhaust gases from the Sinter Cooler first enter a mechanical dust collection device and then a well-designed WHRB to generate Superheated or Saturated steam, as per the plant requirement. Even after the WHRB recovering maximum heat feasible technically, the existing gases have large amount of low grade heat. This heat is recovered by a Hot Water Heat Recovery Unit (HW HRU) downstream the WHRB, as hot water circulating in a closed loop system. The steam thus generated could be put to use in the plant and the Hot water is used as energy source for Vapour Absorption Chiller. The system is well-equipped with necessary instrumentation and a PLC based system for safety & controls, monitoring and diagnostics. Downstream of these systems, an Electro Static Precipitator is provided prior to gases exiting through Chimney.

Major Benefits:
- Cash savings from Energy Savings – Free Steam and Chiller capacity.
- Lower cost of ESP & Downstream system due to lower dust concentration in gases.